Understanding and Managing Inner Knee Pain: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment

Dr. Craig Smith, MD
4 Min read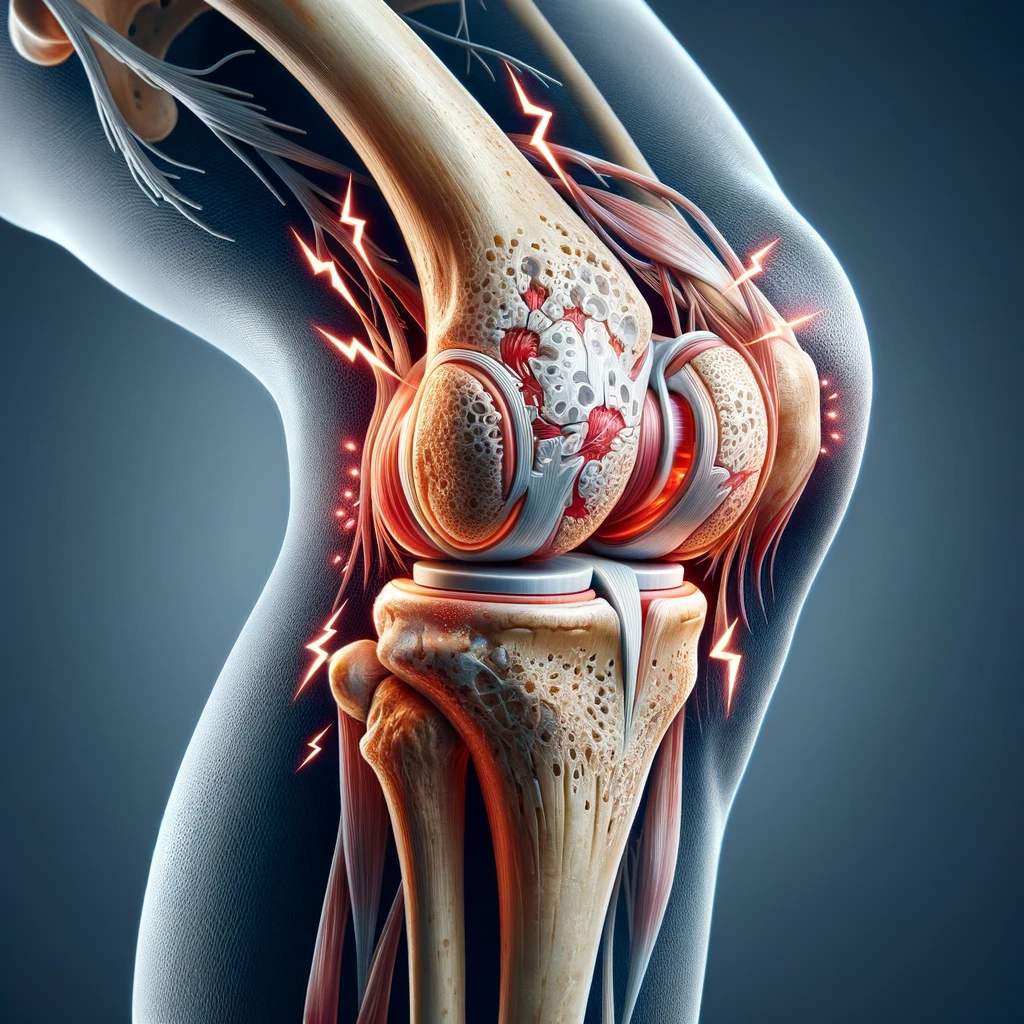
Inner knee pain is a common complaint that can affect individuals of all ages and activity levels. This discomfort can arise from various causes, ranging from overuse injuries to underlying medical conditions. In this article, we will explore the anatomy of the knee, common causes of inner knee pain, associated symptoms, and effective treatment options to alleviate and prevent this condition.
Anatomy of the Knee:
To understand inner knee pain, it's essential to grasp the complex anatomy of the knee joint. The knee consists of three main components: the femur (thigh bone), tibia (shin bone), and patella (kneecap). Ligaments, tendons, and cartilage work together to facilitate smooth movement and provide stability to the joint. The inner part of the knee is particularly susceptible to pain due to the proximity of crucial structures like the medial collateral ligament (MCL), medial meniscus, pes anserinus tendon, and other supporting tissues.
Common Causes of Inner Knee Pain:
- Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) Injury: Injuries to the MCL often occur due to a direct blow to the outer knee or a force that causes the knee to buckle inward, leading to inner knee pain.
- Medial Meniscus Tear: Tears in the medial meniscus, often caused by twisting or sudden pivoting movements, can result in localized inner knee pain, swelling, and limited range of motion.
- Osteoarthritis: Wear and tear of the knee joint can lead to osteoarthritis, causing pain, stiffness, and inflammation in the inner knee.
- Pes Anserine Bursitis: Inflammation of the pes anserinus bursa, often due to overuse or repetitive stress, can result in inner knee pain.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): In RA, the synovium becomes inflamed, leading to pain, swelling, and potentially affecting the inner knee.
- Medial Plica Irritation: Irritation or inflammation of the plica can cause inner knee pain and discomfort.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of inner knee pain can vary depending on the underlying cause but may include pain on the inner side of the knee, swelling and inflammation, limited range of motion, instability or weakness in the knee, clicking or popping sensations, and difficulty bearing weight on the affected leg.
The Importance of Strengthening Muscles:
In addition to addressing the specific causes of inner knee pain, it's crucial to highlight the importance of strengthening the muscles surrounding the knee joint. Strengthening exercises for the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calves contribute significantly to knee stability and overall joint health.
Treatment Options:
- Rest and Ice: Give your knee time to heal by avoiding activities that worsen the pain. Applying ice can help reduce inflammation and alleviate discomfort.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can provide exercises to strengthen the muscles around the knee, improve flexibility, and enhance overall joint stability.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help manage pain and reduce inflammation. In cases of RA, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) may be prescribed.
- Bracing and Support: Depending on the cause of the inner knee pain, using braces or supportive devices may help stabilize the joint and prevent further injury.
- Surgical Intervention: In severe cases or when conservative measures fail, surgical options such as arthroscopy, meniscus repair, or ligament reconstruction may be considered.
Prevention:
To reduce the risk of inner knee pain, consider the following preventive measures: warm-up before engaging in physical activity, gradually increase the intensity and duration of exercise, wear proper footwear and use appropriate equipment, and maintain a healthy weight to reduce stress on the knee joints.
Conclusion:
Inner knee pain can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life. Identifying the underlying cause, implementing appropriate treatment, and incorporating muscle-strengthening exercises are crucial for managing and preventing recurrent episodes of pain. If you experience persistent or worsening symptoms, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment plan.