Complexity of Psoriasis: Causes, Diagnostics, Symptoms, Treatments, and Beyond

Dr. Craig Smith, MD
4 Min read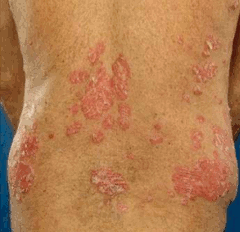
Psoriasis, a chronic autoimmune skin condition affecting millions globally, stands as a testament to the intricate interplay between genetic predisposition and environmental triggers. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the multifaceted realm of psoriasis, unraveling its causes, diagnostics, symptoms, treatments, and additional dimensions that impact individuals living with this condition.
Causes of Psoriasis: Psoriasis, though not fully understood, is recognized as a result of both genetic and environmental factors. Genetic predisposition plays a pivotal role, with individuals having a family history of psoriasis being more susceptible. The environment further contributes to the development or exacerbation of psoriasis, with stress, infections, and specific medications acting as potential triggers. Understanding this intricate balance is crucial in comprehending the complexity of psoriasis.
Diagnostics: Diagnosing psoriasis is a nuanced process involving a meticulous examination of medical history, a comprehensive physical assessment, and, in some cases, laboratory tests. Dermatologists, often at the forefront of diagnosis, rely on the identification of characteristic symptoms – red, raised, and scaly patches of skin. A skin biopsy may be conducted to confirm the diagnosis, ruling out other conditions that might mimic psoriasis. This diagnostic journey underscores the importance of a thorough and individualized approach.
Symptoms of Psoriasis: Psoriasis presents in various forms, ranging from mild to severe. The most prevalent form, plaque psoriasis, manifests as raised, red patches covered with silvery-white scales. Guttate, pustular, inverse, and erythrodermic psoriasis each bring their unique set of symptoms, adding layers to the challenges faced by individuals. Beyond the physical manifestations, the emotional and psychological toll cannot be overlooked. The visibility of the condition may contribute to self-consciousness, anxiety, and depression, emphasizing the need for a holistic understanding of psoriasis.
Types of Psoriasis: A deeper exploration into the various types of psoriasis reveals nuances that influence both diagnosis and treatment. Guttate psoriasis, commonly triggered by respiratory infections, contrasts with the blistering pustular psoriasis, while inverse psoriasis affects skin folds. Erythrodermic psoriasis, though rare, demands specialized attention due to its severity. Recognizing these distinctions is vital for tailoring effective treatment plans.
Psoriatic Arthritis: The link between psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis adds another layer to the complexity of this condition. Approximately 30% of individuals with psoriasis develop psoriatic arthritis, a condition characterized by joint inflammation. This connection highlights the importance of a holistic healthcare approach, addressing both skin and joint manifestations.
Impact on Quality of Life: Beyond the visible symptoms, psoriasis significantly impacts an individual's emotional and psychological well-being. Relationships may be strained, self-esteem affected, and daily activities hindered. Acknowledging and addressing the broader impact on quality of life is paramount, encouraging a comprehensive approach that integrates mental health support into psoriasis management.
Treatments for Psoriasis: While a cure for psoriasis remains elusive, various treatment options aim to manage symptoms and improve overall well-being. Topical treatments, phototherapy, oral medications, and biologics offer diverse approaches, with each tailored to the severity of symptoms. The evolving landscape of psoriasis research continually introduces new possibilities, providing hope for enhanced management and improved quality of life.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies: In addition to conventional treatments, some individuals explore alternative or complementary therapies. Acupuncture, dietary modifications, and herbal supplements are among the options considered. However, it's crucial to approach these with caution and consult healthcare professionals to ensure compatibility with existing treatment plans.
Emerging Research and Future Outlook: Ongoing research endeavors delve into the genetic and immune system intricacies of psoriasis. As the scientific community unravels the complexities, newer treatments and therapies emerge, promising more targeted and effective approaches. The evolving landscape of psoriasis research offers hope for the future, emphasizing the dynamic nature of advancements in psoriasis care.
Support Networks and Resources: Navigating the challenges posed by psoriasis is not a solitary journey. Support networks and patient advocacy groups provide invaluable connections, shared experiences, and emotional support. Access to resources such as educational materials and online forums empowers individuals to actively manage their condition and fosters a sense of community.
Preventive Measures: While psoriasis cannot be entirely prevented, incorporating preventive measures into daily life can contribute to overall well-being. Stress management techniques, maintaining a balanced diet, and identifying personal triggers are proactive steps that individuals can take to potentially reduce the frequency and severity of psoriasis flares.
Conclusion: In unraveling the complexity of psoriasis, it becomes evident that this condition transcends the boundaries of dermatology, impacting various aspects of an individual's life. A holistic understanding of psoriasis, encompassing its causes, diagnostics, symptoms, treatments, and additional dimensions, is essential for both healthcare providers and individuals navigating this chronic autoimmune skin condition. As research continues to advance, the future holds promise for more targeted and effective approaches, providing hope for an improved quality of life for those affected by psoriasis.